You want to build a storage system, your data is 100TB and you suppose you need 100TB storage capacity. Are you sure you are right? How to define the size of your storage system? Especially if you need scalability and redundancy? Boyan Ivanov, CEO of StorPool gave a brief talk on this topic “Provisioned, Usable and Raw Storage – Storage Capacity”. He shines some light on all the main differences between the three types of storage and explains why it is important to look closely at those numbers when communicating them to your storage vendor and analyzing your storage needs.
Raw storage capacity
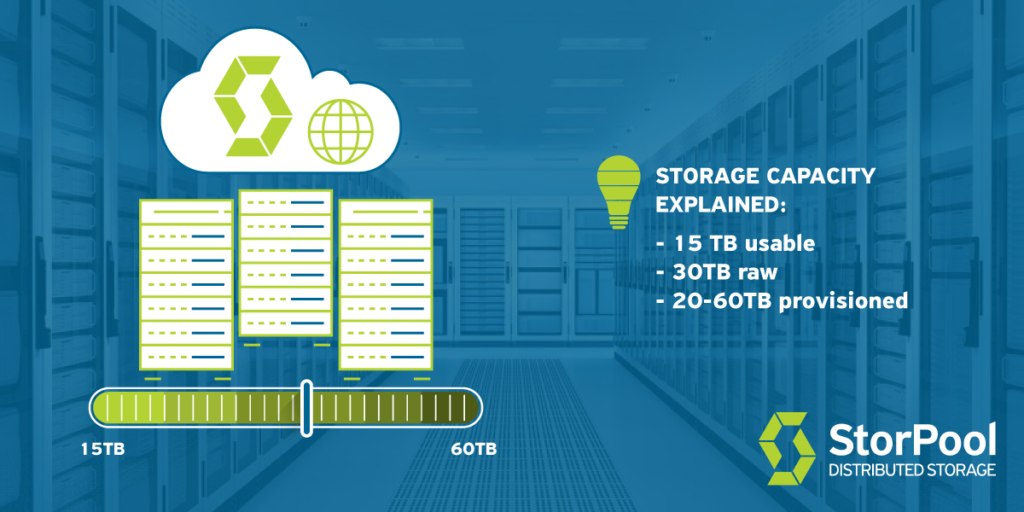
The raw storage capacity shows the actual storage capacity of a storage system. It is based on the devices in that particular system. In the example given by Boyan, if we take 15 SSD’s, each being 2TB, that equals 30TB of raw capacity in the storage system. Most storage systems use a protection scheme of some sort. It guarantees the redundancy and reliability of the data. This can either be RAID 10 or replication, which is the case with the software-defined storage systems. That can decrease three times the default replication level for software-defined storage systems.
Usable storage capacity
With that being said, the example given above can give you 10TB/15TB usable storage, respectively for RAID 10 and software-defined storage. This, simply put, is all the data that can be stored in the system or as we call it – usable storage.
Provisioned (logical) storage space
Because these days over 80% of the workloads are virtualized, it should be taken under consideration how much data exactly can be provisioned on a virtual machine. That is known as a provisioned or logical space. Which actually is the sum of all the virtual disks. In the storage systems, the amount of data you are able to save depends on the space-saving features, implemented in the storage system. Such features may include thin provisioning, snapshot, clone, etc. Additionally, important role plays the type of data itself.
If we go back to the example of 10TB usable space, that would equal 20-60TB provisioned (logical) space. To summarize, the difference is rather big, thus you should always pay attention to which numbers you are looking at. So you can get the perfect machine, satisfying the needs of your business.
Check out our Youtube channel to find more useful videos, advice and more about StorPool.
If you have any questions feel free to contact us at info@storpool.slm.dev